“How do electric scooters work” is a common question among electric scooter beginners. In this guide, we will answer it completely.

How do electric scooters work? (quick answer)
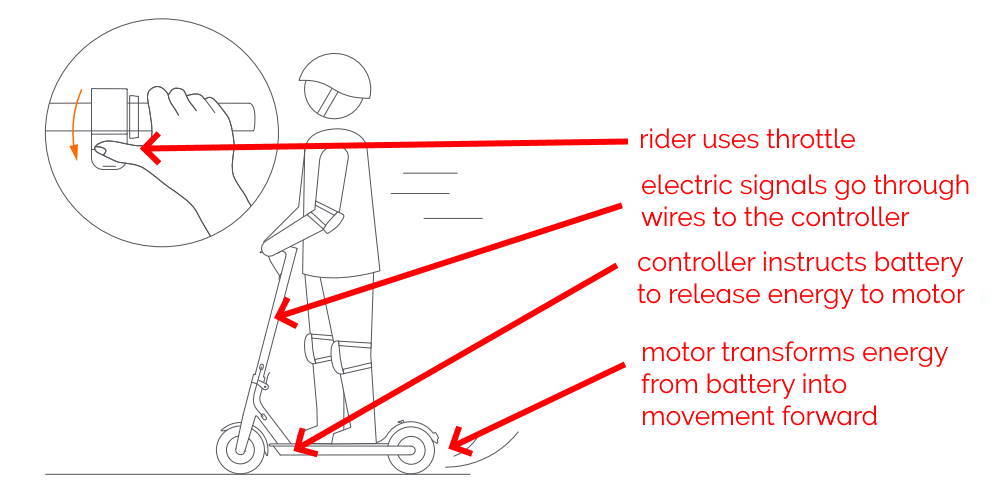
When the rider uses the throttle, an electric signal is sent to the controller, instructing the battery to power one or two wheel motors, propelling the electric scooter forward.
Electric scooter components

Electric scooter technology depends on three major components: the battery, the motor (or motors), the throttle, and the controller.
The battery is the heart of every electric scooter. Its voltage, charge, and energy storage capacity will be the dominant factor in determining the most important features of the scooter, which are the overall performance, and the maximum distance it can go on a single charge.
The motor is of equal importance to the battery. Its power and quality will determine a lot about the scooter’s performances, primarily its speed, its torque, its ability to climb hills, and its range to a lesser extent.
The motor and the battery are connected through electric wires, all controlled by the screen and throttle on the handlebar. Their performance is managed by the rider through the controller component.
Riders use the screen, throttle, and brakes to control the scooter.
Old scooters have deck motors, using chains and gears. Modern ones have gearless hub motors. Powerful scooters often sport two motors.
Wheels come in air-filled or solid types, some with shock absorbers for extra comfort. Scooters have brakes on one or both wheels, electronic or mechanical with disc/hydraulic, or foot-activated.
The components are integrated into a sturdy frame, typically aluminum alloy or carbon fiber, with a foldable frame.
Most scooters include a headlight and rear lights, some as brake lights.
How does an electric scooter work?
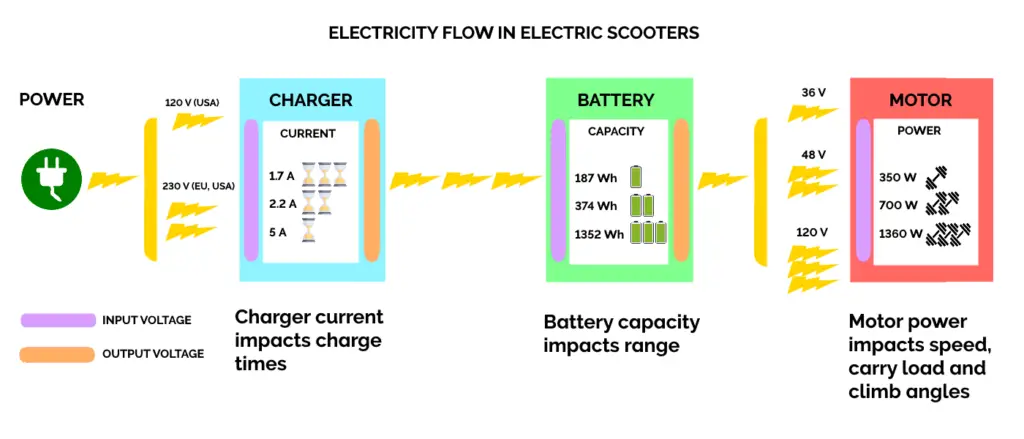
When the rider presses the throttle, it sends a signal to the battery to release power. The battery sends the power to the motor (or motors) through the wires. The motors then produce a movement of the wheels and propel the scooter forward.
Electric scooters can’t go in reverse, and the only way to move is forward, through the throttle. Scooters have one or more brakes that slow down and stop the scooter.
How do electric scooter motors work?
As mentioned before, scooters can have their motors live inside the deck, which requires them to connect to the wheels through gears and chains.
Newer scooters, however, have the motors integrated into the wheel itself, which is a much more robust and foolproof design.
Batteries provide direct current (DC), so all motors in electric scooters are DC motors.
DC motors come in two basic flavors – brushed and brushless.
Brushed motors generate power by two sets of electromagnets. One is cylindrical, and the other one is a smaller magnet inside the cylinder. When the inside is turned, it generates magnetic fields that cause the inside to continue turning and generate power.
Of course, the details of how a brushed DC motor works are a bit more complex.
Brushless DC motors are a more modern technology that is an improvement over brushed DC motors. Brushed motors have an efficiency of about 75-80%, while brushless have an efficiency of about 85-90%.
The way a brushless motor works is almost like an inverse brushed motor. The magnets that move in the brushed motor are the parts that don’t move in the brushless motor. Again, the details of how a brushless motor works are more complex.
Brushed motors require a bit more care and maintenance since the brushes wear off over time. On the other hand, some brushed motors offer regenerative braking capabilities, which is a nice feature to have.
Chances are, if you’re getting a new scooter, it will have a brushless motor.
The amount of power your motor will generate will be expressed in Watts (W). Common scooters have between 200 and 600 Watts, but there are scooters that have much, much more.
Keep in mind that if your scooter has less than 300 Watts, it will likely have trouble climbing steeper hills.
The top speed will greatly depend on the motor power as well. While this is not a precise formula by any means, and there will be many other factors that determine the max speed you can get out of your scooter, you can expect 1 km/h for every 10-20 W of power your motor has. This doesn’t apply to the most powerful scooters, but it’s a good estimate for the consumer-grade ones.
One other thing worth knowing – the motor power can vary over time.
Most of the time it is around a certain baseline, and this is what it’s called its real power. This is the power level you will likely get most of the time.
However, at certain times, the motor can exceed that power level and reach much higher ones. The maximum power the motor can reach is called peak power.
Manufacturers can do a somewhat cheap trick and report the peak motor power as its real power. Make sure you double-check that and look at the real power, it’s a much better representation of how much power the motor really has.
If you are interested in learning more about the details (real vs peak power, geared vs gearless, brushed vs brushless), check out the full article on electric scooter motors. Also, if you want a quick way of figuring out what the estimated peak power of your motor is based on the real one, or the other way around, check the real and peak motor power converters.
How do electric scooters batteries work?
Most electric scooters will have lithium-ion batteries. The best scooters will typically come with either Samsung or LG batteries.
The most important metrics about the battery are:
- its voltage, which we express in Volts (V)
- its charge, which we in Ampere-hours (Ah)
The higher the voltage, the more power will the battery be able to supply to the motor.
The bigger the both, the more energy storage capacity will the battery have. We express energy storage capacity in Watt-hours (Wh), and we obtain it by multiplying the Volts times the Ampere-hours.
1 WH = 1 V * 1 Ah
The formula for energy storage capacity
These are the simple calculators you can use to convert between these units:
The bigger the capacity, the more range your scooter will have. Of course, it’s not the only factor, but it is the most important one.
While not an exact formula, you can think of it like this: every 10-20 Watt-hours will give your scooter 1 kilometer of range.
Batteries degrade over time, and you will likely need to replace the battery in your scooter every time it gets worn out. This will happen every 3 years on average.
It is also possible to upgrade your battery to a more powerful one, or add an extra battery (or two). This will further increase the range you get to a great extent, and it may also improve speed and general performance as well.
You can learn all the tips and answers about electric scooter batteries in the full battery guide.
How do controllers in electric scooters work?
The controller in the electric scooter is the glue between the acceleration and brake controls, the battery, and the motor.
Whenever you hit the throttle, the signal goes through the wires and through the controller, which tells the battery to release more or less energy to the motor. If your scooter has electronic brakes, it stops the juice from the battery and instructs the motor to stop working.
How do brakes in electric scooters work?

There are three types of brakes in electric scooters.
The most basic one is the rear foot brake, where you just press against the rear fender with the foot to create friction. It is also the least practical way to brake, since it requires you to hit the rear fender with your foot, preferably without looking back. However, not a lot of scooters have this brake type.
Another way to brake is through the old and trusted mechanical brake, which is usually either disc or hydraulic. Scooters like this will usually have a lever on the left handle, which when pressed activates the disc brake on either the front, the rear wheel, or both.
The third and most advanced braking method is an electric brake. These are fairly common, and they work almost as exact negatives to the acceleration process as they stop the motor from producing movement.
Scooters with this type of braking also employ regenerative braking. This braking method refills the battery a little every time it’s activated.
Obviously, the more brakes a scooter has the better, but very few have all three. A combination of disc and electrical braking is a great combination.
How do wheels in electric scooters work?
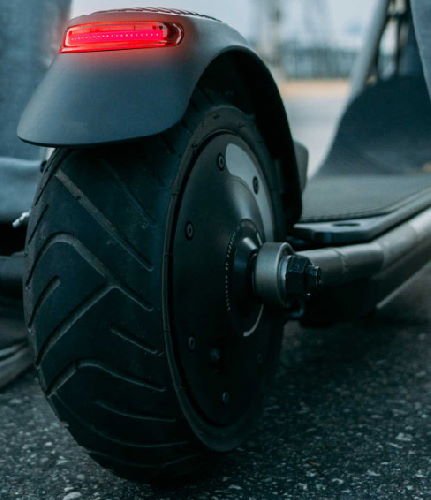

There are two types of wheels that an electric scooter can have – solid and air-filled (pneumatic).
Solid wheels are not very common. The upside of solid wheels is that they can’t get punctured and there are no flat tires with them. The downside of solid wheels is that the ride will be more shaky and bumpy. That’s why it’s scooters with solid wheels usually have good suspenders.
Air-filled tires are the opposite – you can occasionally get a flat that you will have to fix, but they provide a more comfortable ride. That’s why suspenders in scooters with air-filled tires are less common.
Also, air-filled tires are usually less slippery since the rubber provides more friction against the ground. You can also inflate or deflate them to adjust for speed vs control.
Wheels can come in several patterns and sizes.
Wheels for everyday use are slicker and provide a faster ride, while off-road wheels have perforations and holes in them that make them better for handling rough or uneven terrain. Many scooters can support both road and off-road tires.
The size of the tire itself will determine a few things about your scooter too.
Scooter with wide wheels provide better control, increased acceleration, and reduced braking distances. The downsides will include less comfortable rides, increased battery consumption, and faster wear and tear.
Some scooters have a combination of one solid and one pneumatic wheel, but those are not common. A few scooters offer both types of tires, and you can swap solid and pneumatic tires with relative ease.
How does suspension in electric scooters work?
Some scooters have suspension systems on their wheels for increased riding comfort and less shaking. It often comes with electric scooters with solid tires, to compensate for the decreased stability and comfort that solid tires provide.
Usually, scooters have either spring arm or hydraulic suspensions. Spring suspensions are simpler, but they work well on many models. Hydraulic suspension systems are more complex and even involve dampers with hydraulic fluid, but this mechanism is usually top-notch and only the higher-quality scooters include it.
How do electric scooter screen and controls work?

Most electric scooters have an LCD screen at the center of the handlebars, and it sometimes has only one button, which is the power button. Other scooters use a circular device on the right handlebar.
You will use the screen for several things. Depending on the number of times and how long you press it, it can:
- power the scooter on and off
- change the driving mode
- show you other information about the scooter, like its battery level
The power button and the throttle are sometimes the only controls the scooter has, unless it has a brake lever too.
Some scooters are started by keys and don’t use the screen to start.
Optionally, the scooter may have a horn or a bell to notify or alert other participants in traffic.
Electric scooter deck
The deck’s key attributes are size, height (ground clearance), and grip.
Size varies but affects comfort and stability. Taller riders or those with big feet prefer wider decks.
Height impacts stability and obstacle clearance. Higher clearance helps overcome obstacles but raises the scooter’s center of gravity, reducing stability.
Grippy decks enhance traction through rubber bumps or sandpaper-like materials.
Electric scooter handlebars

Handlebars steer the scooter. Some offer height adjustment.
Most have non-slip rubber/silicone grips for safety. Throttle’s typically on the right, brake on the left if available, with the screen in the middle.
Few models cater to left-handed riders with the throttle on the left and the brake on the right.
Electric scooter lights
Almost every electric scooter will come with at least a LED headlight, and some will come with a tail light that is activated when braking.
Lights are a big drain on the battery, and maybe that’s the reason why some scooters only come with very weak lights.
Some scooters will also have LED lights on the sides or the bottom of the deck.
Optional scooter parts
Aside from the essential parts that pretty much every electric scooter will have, some scooters may have an extra feature or two that can make it much more useful.
Seats

For many scooters, seats are an optional addition. You will usually pay a bit extra, but your scooter can become much more useful. Many scooters with seats come with the option to add or remove the seat as you need.
Baskets or trunks
In my opinion, true adult scooters have a basket or a trunk. The ability to use your scooter as more than just a person-transporting vehicle can be invaluable in your day-to-day activities.
However, not a lot of scooters come with a built-in way to install a basket or a trunk. While possible, the process does involve some customization, and for some models, it can be infeasible because of the overall construction and balance of the scooter. You can see some great scooters with trunks here.
How do electric scooters get charged?
Charging an electric scooter is simple, but there are a few steps that make it optimal and can potentially increase the lifespan of your scooter’s battery, and ultimately your scooter:
- let your scooter cool off before charging
- use only the original charger
- charge in a cool, dry room, at room temperature
- charge until full as often as possible
- don’t let the battery get empty
Check out the post on how to charge your scooter to see every charging hack and tip available.
Are electric scooters foldable?
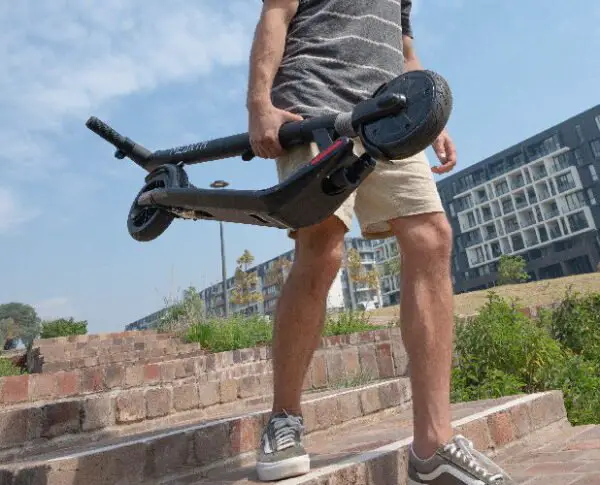

Most of today’s electric scooters will be foldable. Some older models, or scooters that are clearly not meant to be carried (like very heavy scooters) may not include a folding mechanism, and that is a significant disadvantage for those models.
Folding mechanisms vary, but a common one involves a stem latch, making scooters portable and space-saving.
Surprisingly, the folding mechanism, though seemingly simple, can be a major frustration for owners due to loosening or malfunction.
Certain models have foldable handlebars for even more compact storage.