Electric scooter batteries are vital, affecting speed, range, and cost efficiency. This guide ensures responsible ownership and longevity.

Electric scooter batteries – what you need to know
Electric scooters run on electric batteries, mainly Lithium-Ion ones, with voltages ranging from 24 V to 120 V. These batteries usually have between 150 Wh and 750 Wh of energy and take about 8 hours for a full charge, lasting an average of 2 to 3 years.

What kind of battery does an electric scooter use?
Most electric scooters today use lithium-ion batteries, which offer significant advantages over other types of electric batteries:
- they have higher densities, which give the scooters longer ranges
- they have a slower self-discharge rate (meaning they don’t drain as fast when not used)
- they don’t require a lot of maintenance
- higher voltage than other electric batteries
- they don’t suffer from the memory effect (losing efficiency after partial charges)
- a few other advantages such as no need for priming (charging the battery slowly and discharging it fully for the first few times) etc
However, lithium-ion batteries also have several disadvantages you need to be aware of:
- they shouldn’t be fully discharged
- they age and become very weak after 500-1000 charges, even with little usage
- taking a lithium-ion battery on an airplane is a drag
- batteries can catch fire and explode
There are several types of lithium-ion batteries, depending on the active material that’s bonded with the Lithium atom:
- Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO2) – LCO (used in mobile phones, tablets, laptops, cameras)
- Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn2O4) – LMO (power tools, medical devices, electric powertrains)
- Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (LiNiMnCoO2) – NMC (E-bikes, medical devices, EVs, industrial)
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) – LFP (Portable and stationary devices that need high load currents and endurance)
- Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (LiNiCoAlO2) – NCA (Medical devices, industrial, electric powertrain (Tesla))
- Lithium Titanate (Li2TiO3) – LTO (UPS, electric powertrain (Mitsubishi i-MiEV, Honda Fit EV), solar-powered street lighting)
The most common type found in electric scooters is Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC).
Some models of electric scooters, especially older ones, have different types of batteries, usually lead-acid or nickel-metal-hydride batteries.
Which battery is best for an electric scooter?
Lithium-ion batteries are ideal for electric scooters due to their high energy density, lack of memory effect, and ease of maintenance.
Also, the battery manufacturer matters.
My electric scooter came with a generic Chinese battery that worked well initially, but after a few months, its performance significantly declined, affecting the range and top speed.
To enhance my daily commute, I upgraded to an LG battery, resulting in remarkable improvements.
Top brands like Samsung, LG, and Panasonic perform well. European/Japanese/Korean brands are mid-high quality (e.g., Sanyo, Toshiba). Chinese brands (Amperex, BYD, BAK Group, AESC, CATL) are improving but generally not on par with top-tier brands.
Avoid generic low-quality Chinese batteries as they degrade quickly. Tesla mainly uses their batteries in vehicles, making scooter integration uncertain.
Only a few models still employ lead-acid batteries today.
Electric scooter battery specifications (voltage, charge, and capacity)
| Specification | Metric |
|---|---|
| Input voltage | Volts (V) |
| Output voltage (or just voltage) | Volts (V) |
| Charge | Ampere-hours (Ah) |
| Capacity / energy | Watt-hours (Wh) |
Understanding these three key measurements is important, and they’re quite straightforward.
The three measurements about the battery you need to know are:
- voltage
- charge capacity
- energy storage capacity
Electric scooter battery voltage
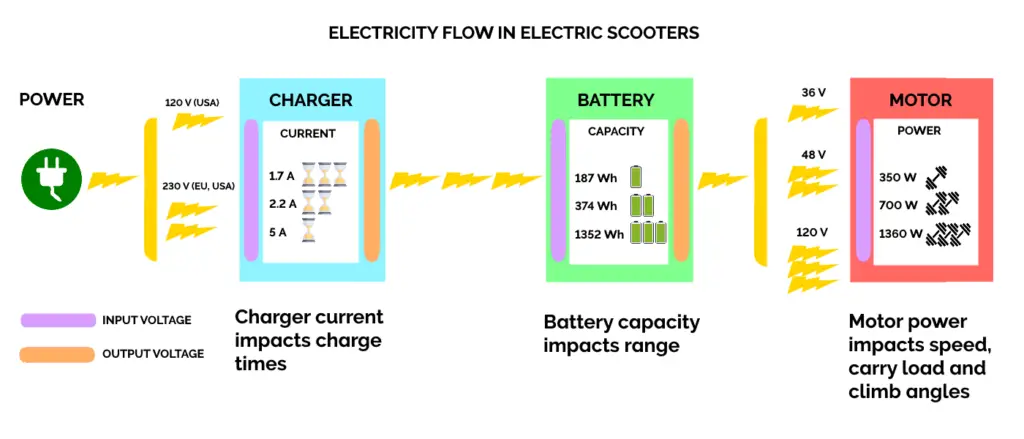
Voltage is what forces the electrons to move through the circuit, forcing an electric current. We measure voltage in Volts (V).
It measures how fast can power be released. The higher the voltage is, the faster a battery can provide more power to the motor.
Batteries typically have two types of voltage: input and output.
When discussing battery voltage, we usually mean the output voltage, which should be a few Volts higher than the motor’s input voltage.
Scooter batteries commonly range from 24 V to 48 V, with some going up to 96 V or 120 V. You can calculate a battery’s voltage by dividing its capacity (in Watt-hours, Wh) by its charge (in Amp-hours, Ah).
Formula: 1 V = 1 Wh / 1 Ah
You can use the battery voltage calculator as well.
Electric scooter battery charge
Charge can be simplified into two types: positive and negative.
All matter consists of atoms, made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Extra electrons result in a negative charge, while fewer electrons lead to a positive charge. Objects with extra electrons are negatively charged.
Electricity is the flow of electrons, so batteries need electrons (charge) to generate electricity.
Battery charge is measured in Ampere-hours (Ah).
Battery charges in electric scooters can range from 4 Ah all the way up to 50 Ah in the most powerful scooters.
If you know the battery’s voltage and capacity, you can find out its charge by dividing the capacity measured in Watt-hours (Wh) by the voltage measured in Volts (V).
Formula: 1 Ah = 1 Wh / 1 V
You can also see the battery Amp-hours calculator in a foolproof way.
Electric scooter battery capacity
To determine energy storage capacity, multiply the voltage by the charge capacity. Manufacturers often provide only voltage and charge info, as energy storage is simply how much energy a battery can store, measured in Watt-hours (Wh).
One Wh equals one Volt multiplied by one Ampere-hour. Scooter batteries typically range from 100 Wh to nearly 3000 Wh, with most adult scooters having capacities between 150 Wh and 624 Wh.
If you know the battery’s charge and voltage, you can find out its capacity by multiplying the two.
Formula: 1 Wh = 1 Ah * 1 V
You can also use the battery capacity calculator.
Are electric scooter batteries safe?

Electric scooters use the same batteries as laptops and other devices, typically safe due to rigorous testing. Yet, accidents can occur due to misuse or manufacturer defects, such as fires and explosions.
To mitigate these risks, electric scooter batteries incorporate battery management systems. These systems ensure proper charging, discharge, and safeguard against issues like overcharging, overheating, or fires.
To increase battery safety, follow the best practices for battery storage and handling. The most important steps are:
- purchase batteries from a reputable manufacturer or supplier
- avoid batteries shipped without protective packaging (hard plastic or equal)
- inspect batteries upon receipt, and visually inspect them at least once a week
- be careful not to damage the battery casing or connections
- store batteries away from combustible materials
- remove batteries from the device for long-term storage
- store the batteries at temperatures between 5°C and 20°C (41°F and 68°F).
- charge batteries in storage to approximately 60% of capacity at least once every month,
- if batteries smell weird, get heated, or change shape, disconnect them immediately, and then dispose of them
- don’t overcharge batteries
- keep batteries from contacting conductive materials, water, seawater, strong oxidizers, and strong acids.
- do not leave batteries under the sun or in hot locations
- keep batteries away from flammable materials
- do not charge immediately after riding, or ride immediately after charging, give the battery some time to cool off
How do you charge an electric scooter battery?

These are the universal steps to charging your e-scooter battery:
- use only the scooter’s original charger
- insert the charger into the power outlet
- insert the charger head into the charging port of the scooter
- wait until the battery is fully charged (every scooter will have different ways of indicating this)
- remove the charger head from the charging port of the scooter
- finally, unplug the charger from the power outlet first
Refer to your scooter’s manual for instructions. If none are provided, follow these steps in order.
Manual instructions take precedence over these. Use the original charger or a matching one from the same manufacturer to avoid battery degradation.
Charge your battery when it’s below 15%, but never let it fully discharge to extend its lifespan. If storing your scooter, ensure the battery stays around 60% charged by charging it at least once a month.
Make sure to check out the full guide to charging your electric scooter for tips that even most manuals don’t include.
Typical electric scooter ride times range from 30 minutes to 6 hours, with average use lasting around 2 hours. At maximum speed, expect around 50 minutes, but it can be as short as a few minutes or up to 2.5 hours, depending on the model.
A more relevant metric is the scooter’s range, averaging 28 miles (46 km) and varying from 4 to 93 miles (7 to 150 km)
How long does an electric scooter battery last?
Electric scooter batteries generally last between 2 and 3 years, but can range from a few months to 5 years. They endure around 300 to 500 charge cycles, with performance decline sometimes noticeable after 150 cycles.
How long a battery lasts will depend on:
- the type of battery
- the year when it was produced
- the brand and manufacturer
- how well you take care of it
There are a few things you can do to extend the lifespan of your battery.
To maintain your electric scooter’s battery, charge it regularly, avoid complete discharge, and store it between 0°C to 45°C, ideally 5°C to 30°C, to extend its life.
Electric batteries naturally degrade over time, but these tips help maximize their lifespan. Plug in your charger to check if a battery is working – a green indicator light means it’s charging correctly.
Visually inspect the battery for damage, leaks, burns, or anomalies, but be cautious as it may require deck disassembly and could void your warranty on some scooters.
Some newer models feature removable batteries, offering a convenient option for visual inspection. See my detailed guide on scooters with removable batteries if you want to find out more about this exciting new feature.
How to test an electric scooter battery with a voltmeter or a multimeter?
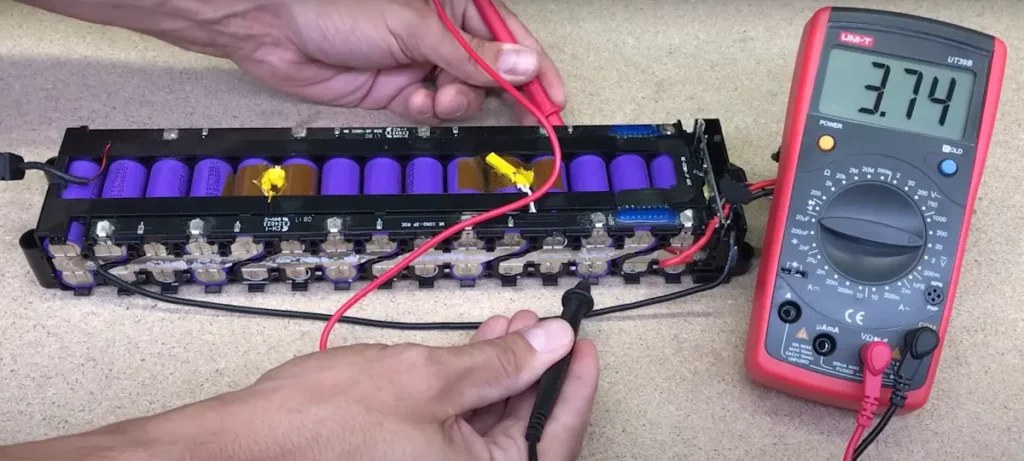
These are the steps to test an electric scooter battery with a multimeter:
- Fully charge your scooter
- Plug the multimeter cables
- Set the multimeter to DC Volt 200
- Turn off your scooter
- Place it on something so that the wheels hang in the air, for example placing the deck on a small chair
- Open the scooter’s deck
- Connect the cables to the battery’s ports, ensuring proper metal contact
- Turn on your scooter and the multimeter
- Compare the multimeter reading to the battery’s voltage; it should be the same or slightly higher
- A lower reading suggests battery wear
- For a load test, throttle while the wheels are off the ground
- The multimeter reading should match or slightly exceed the original battery voltage, a smaller reading indicates degradation
When do I need to replace my electric scooter battery?
Batteries wear out over time, and after a while, you will have to replace them.
The first sign that you need to replace the battery in your scooter will be reduced range. Battery performance is proportional to range, and when the range of your scooter drops to 50% or less of its original range, it may be time for a replacement.
Reduced top speed and climbing capabilities are a strong indicator too.
How much do electric scooter batteries cost?
The battery is one of the most valuable parts of the scooter.
Replacing it can cost anywhere between 15% and 30% of the original price of the scooter.
Can you upgrade your electric scooter’s battery?
Your scooter can benefit from a more powerful battery, depending on its motor, controller, and electronics, mainly the voltage.
If the battery’s voltage is significantly lower than the motor and electronics (over 12 volts difference), upgrading to a higher-voltage battery can boost overall performance in range and top speed.
Avoid a higher voltage battery if your current one already matches or closely aligns with the motor or electronics voltage, as it can harm the scooter’s electronics. In theory, upgrading to a higher-capacity battery with the same voltage can extend your range.
However, exercise caution and thoroughly understand your scooter’s internals before making any modifications.
Can you add an extra battery to your electric scooter?
In most cases, you can add an extra battery to your scooter, with some scooters coming prepared with the necessary frame and setup for easy installation.
There are two ways you can add a battery: in series and in parallel.
In series, you boost voltage for more power and speed but ensure it doesn’t exceed the motor and electronics’ limits.
In parallel, you increase the charge for a greater range. A dedicated guide on adding an extra battery is coming soon.
Is an electric scooter battery waterproof?
Most electric scooters are water-resistant and some specify an IP rating for water protection.
However, the battery’s water resistance might differ from the scooter’s overall rating, with a few models offering better battery protection. Roughly half of scooters have official water-resistance ratings.
Unless stated otherwise, the battery shares the scooter’s rating. While some scooters are water-resistant, manufacturers often recommend avoiding wet conditions, including rain and snow, to ensure safety and battery longevity.
To ensure your electric scooter battery’s safety and durability, store it in a dry, dark room with temperatures between 5°C and 20°C. Regularly charge the battery to around 60% capacity and recharge it monthly, even during periods of inactivity. For detailed instructions, consult our storage guide.
Some scooters are suitable for kick-riding, while others are too heavy or have a high deck. If your battery dies mid-ride, you’ll need an alternative mode of transport. For more details, read our guide on using electric scooters manually.
The battery’s charge capacity primarily determines the scooter’s range, while the motor voltage affects its power. More charge capacity means greater range, and higher voltage provides more power. However, the motor’s voltage plays a more significant role in power, and battery voltage usually doesn’t vary significantly.
Battery technology has significantly improved over the last few decades, boosting scooter ranges from just a few kilometers to over 150 kilometers on a single charge. Electric scooters, along with electric cars, have driven these advancements, resulting in better performance and more affordable batteries.