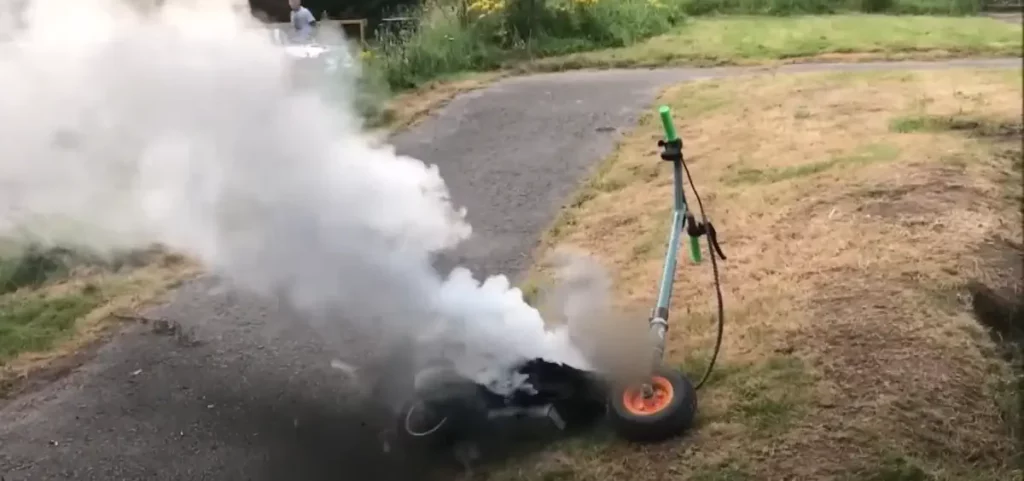
“Are electric scooters catching fire” is a surprisingly common question. Several unfortunate accidents involving e-scooter fires have occurred and continue to happen.
This has made people wonder what causes an electric scooter to catch fire and in this article, we will find out why.

Electric scooter fires
Electric scooters can catch fire at times, but the occurrence of such incidents isn’t as common as it was several years ago. The main reasons why an e-scooter can ignite are using faulty low-quality batteries and improperly charging, and not storing the scooter properly.

Why are some electric scooters catching fire?
Electric scooter batteries are the main cause of fires.
Most electric scooters use lithium-ion batteries, known for high energy density, efficiency, and lightweight design.
Despite their advantages like fast charging and durability, these batteries pose a fire hazard in a small number of cases due to a combustible electrolyte and lithium compound.
Improper manufacturing or management can lead to fires, causing significant damage and potential casualties.
Lithium-ion batteries basics
Now, before I begin explaining in detail why lithium-ion battery failure is the most common cause of electric scooter fires and how a fire can be prevented or stopped, let’s see what a li-ion battery is made of and how it works.
What are lithium-ion batteries made of?
Lithium-ion batteries consist of a cathode (typically lithium cobalt oxide) and an anode (made of graphite), separated by a permeable separator containing a lithium-based salt electrolyte.
How do lithium-ion batteries work?
A lithium-ion battery operates by transferring electrons and lithium ions between electrodes through the electrolyte and an external circuit.
During charging, lithium ions move from positive to negative electrodes, while electrons flow through the external circuit. When there’s no more movement, the battery is fully charged.
Discharging reverses these processes, generating an electrical current for the scooter. Any interference or changes in electrochemical reactions could lead to hazardous incidents.
What causes a lithium-ion battery to catch fire?
Let’s see now why lithium-ion batteries are susceptible to fires.
Construction and design defects
Unscrupulous electric scooter manufacturers may use subpar designs and low-quality materials for their batteries, often skipping quality control inspections.
Failure to adhere to manufacturing standards can result in serious issues like short circuits and thermal runaway, leading to the risk of battery fires.
Damages to the separator during manufacturing can cause an uncontrolled flow of lithium ions and electrons, creating a short circuit and generating excess gas pressure and heat, ultimately contributing to thermal runaway.
Internal short circuit
A short circuit in a lithium-ion battery happens when the cathode and anode are electronically interconnected, causing an uncontrolled current release and a substantial energy delivery.
Prolonged short circuits lead to self-discharge, raising the battery’s internal temperature.
If the temperature surpasses a critical point, electrolyte decomposition occurs, triggering thermal runaway and posing severe safety risks.
Short circuits are usually caused by:
- poor battery design
- overcharging
- poor cell quality
The battery’s content and design
A lithium-ion battery is more prone to catching fire compared to other battery types due to the following reasons:
- Its lithium salt-based electrolyte is highly combustible.
- During charging and discharging, the materials in the cathode expand and contract, which puts stress on the battery. Consequently, it can release oxygen, which is also highly combustible.
- It has a relatively small storage capacity and it stores a considerable amount of energy.
Battery failures
Most lithium-ion battery failures are produced by construction defects, flawed design, improper storage and operation, thermal runaway as well as mechanical and electrical abuse.
Over-discharge
In discharging, lithium ions move from the negative to the positive electrode.
Over-discharging can lead to the dissolution of the negative electrode (anode) in the electrolyte, raising the risk of a short circuit and potential fire due to copper particle dispersion.
Additionally, a short circuit can initiate chemical processes producing combustible gases like oxygen and hydrogen.
Overcharge
A lithium-ion battery requires careful maintenance of safe charge levels for proper operation. Overcharging or fast charging can exceed the battery’s limit, reducing performance or rendering it unusable.
One study has shown that overcharging a Li-ion battery leads to thermal runaway too. Once the battery’s internal heat gets out of control, this inevitably leads to a fire.
Reputable e-scooters typically come with a Battery Management System (BMS) to prevent overcharging or excessive battery depletion.
Impact damage
Electric scooter batteries are usually encased in durable materials, minimizing physical damage.
However, repeated shocks can puncture or break the battery, leading to a short circuit, gas accumulation, and heat, ultimately causing thermal runaway.
A mechanically damaged battery poses an immediate fire risk and can result in defects leading to future fires, highlighting the importance of rider awareness.
Other factors that can damage lithium-ion batteries include:
- very high temperatures (e.g., above 55°C/130°F)
- charging in zero-degree temperatures (32°F)
- using ultra-fast chargers that are not suitable for Li-ion batteries
Water ingress
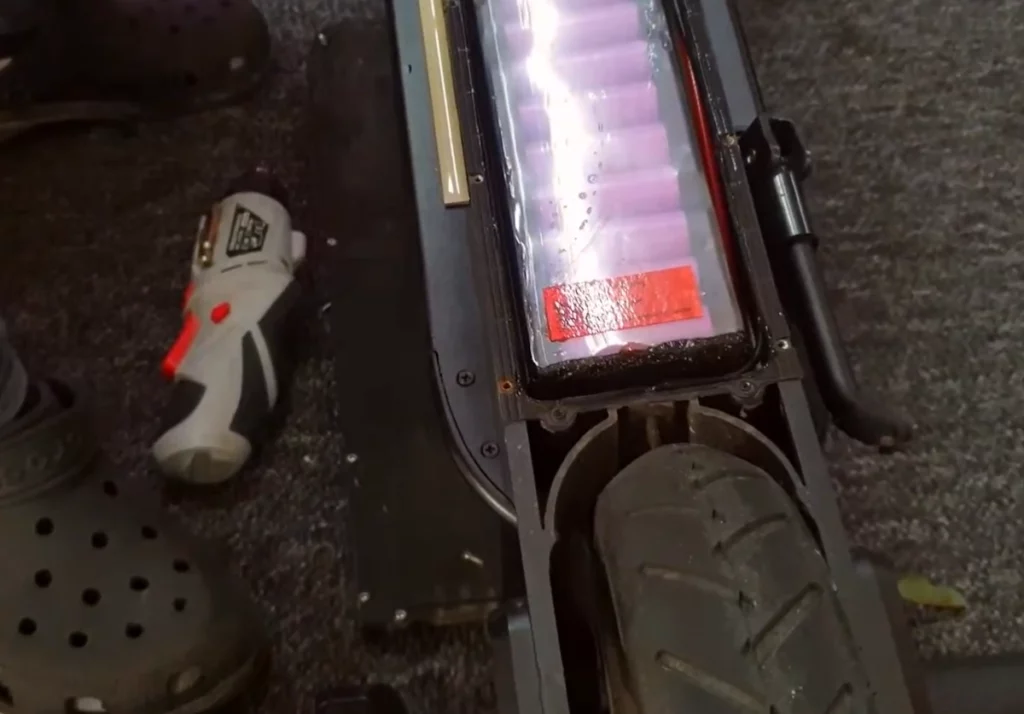

Water-resistant electric scooters with waterproof batteries and casings have minimal fire risk.
However, non-waterproof scooters are more prone to fire hazards.
Moisture entering wire areas can cause metal connections between battery cells to rust, potentially leading to a short circuit and fire.
Exposure to high temperatures
Electric scooters using lithium-ion batteries should be operated in temperatures ranging from 14 F° – 113 F° (-10°C to 45°C).
Higher external temperatures than those inside a Li-ion battery cause the cells to heat.
Once the battery reaches a certain temperature, a reaction occurs between the electrolyte and positive electrode, generating more heat and increasing pressure in the cells.
This pressure can lead to the discharge of content, potentially igniting a fire.
Elevated battery temperature can also produce combustible gases, contributing to the risk of flames.
What is thermal runaway?
Thermal runaway, a chain reaction, happens when a lithium-ion battery self-heats, causing a rapid increase in temperature and pressure with an uncontrolled energy release.
This process results in the dissolution of chemicals, emitting smoke, toxic, and combustible gases, further intensifying heat and culminating in the potential ignition of a fire.
You can find out more information about thermal runaway in the study here.
What causes thermal runaway?
There are several causes of thermal runaway.
However, one study shows that one of the most common causes of this phenomenon is a lithium battery’s internal short circuit.
Other common causes of thermal runaway include:
- overcharging
- undercharging
- overheating
- mechanical damage
- improper use of the battery
- external short circuit
- very low-temperature environments
Thermal runaway prevention
Decreasing battery loading is an essential prerequisite for warding off thermal runaway events. Battery loading includes improper discharging and charging as well as frequent hits and shocks.
Thermal runaway can be prevented in the following ways.
 Using battery management systems (BMS)Modern electric scooters come with Battery Management Systems (BMS) that prevent overcharging, full discharge, and overheating by detecting rapid temperature increases.
Using battery management systems (BMS)Modern electric scooters come with Battery Management Systems (BMS) that prevent overcharging, full discharge, and overheating by detecting rapid temperature increases. Using a sturdy battery pack casing materialMost Li-ion battery packs are enclosed in sturdy plastic or metal casings, such casings help protect battery packs from overheating during discharging and charging.
Using a sturdy battery pack casing materialMost Li-ion battery packs are enclosed in sturdy plastic or metal casings, such casings help protect battery packs from overheating during discharging and charging. Ensuring heat dissipationMethods electric scooter manufacturers use to ensure heat is released from battery packs include: using a fan, using air cooling and wrapping the battery pack in a liquid cooling jacket
Ensuring heat dissipationMethods electric scooter manufacturers use to ensure heat is released from battery packs include: using a fan, using air cooling and wrapping the battery pack in a liquid cooling jacket
How common are electric scooter battery fires?
While the risk of lower-power commuter electric scooters or those from reputable manufacturers catching fire is generally low, all electrical devices pose a potential fire hazard without proper safety measures.
Though incidents have decreased due to improved battery safety features and manufacturing methods, ensuring stricter regulations and standards for electric scooter batteries is crucial for minimizing risks during use, charging, or storage.
Until such measures are in place, guarantees against scooter fires remain uncertain.
How can you tell whether an electric scooter battery is damaged?
Being able to tell if your scooter battery is damaged can protect you from many unwanted occurrences. So, here are several red flags you should look out for.
 Burning smellWhen a battery gives off a foul odor, this is a telltale sign that pressurized gasses are being released and the battery is defective.
Burning smellWhen a battery gives off a foul odor, this is a telltale sign that pressurized gasses are being released and the battery is defective. Extreme heatIf you notice that your scooter battery often releases excess heat, this is a warning sign that it’s going bad.
Extreme heatIf you notice that your scooter battery often releases excess heat, this is a warning sign that it’s going bad.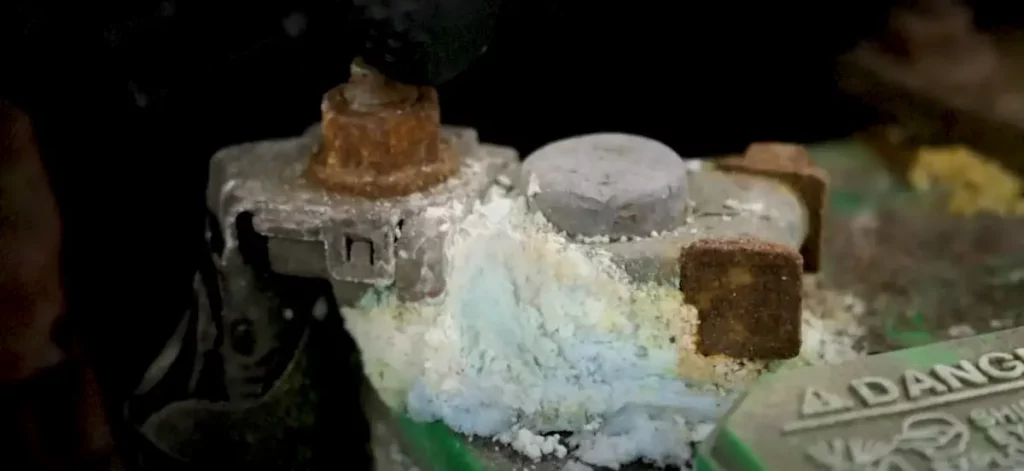 CorrosionIdentify battery corrosion by checking for water drops on the shrink wrap or rusted cable connections, and if you lack experience in disassembling an electric scooter, take it to a workshop or mechanic for inspection.
CorrosionIdentify battery corrosion by checking for water drops on the shrink wrap or rusted cable connections, and if you lack experience in disassembling an electric scooter, take it to a workshop or mechanic for inspection. Swelling or bruisingWhen a battery looks bulged or bent or has even the slightest bruise or dent, this is an indication that’s defective and should no longer be used.
Swelling or bruisingWhen a battery looks bulged or bent or has even the slightest bruise or dent, this is an indication that’s defective and should no longer be used.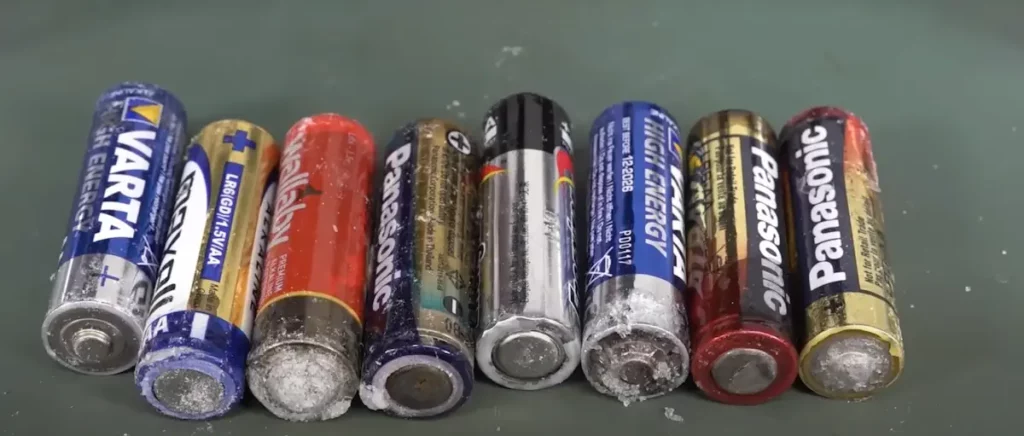 LeakageElectrolyte leakage can lead to serious defects in the electric scooter’s body and electrical system, it’s a grave issue that must not be ignored.
LeakageElectrolyte leakage can lead to serious defects in the electric scooter’s body and electrical system, it’s a grave issue that must not be ignored. Strange noiseIf your scooter battery produces unusual popping or clicking sounds, it indicates potential deterioration or failure in such cases, cease use and replace it immediately.
Strange noiseIf your scooter battery produces unusual popping or clicking sounds, it indicates potential deterioration or failure in such cases, cease use and replace it immediately.
How can you prevent an electric scooter fire?
When it comes to preventing electric scooter fire there are several useful tips on how to minimize the risk of an e-scooter battery fire in different situations.
Charging your electric scooter

When you are charging your electric scooter you should consider the following tips:
- Adhere to the charging times provided in the manufacturer’s instruction manual, especially when you fully charge your e-scooter.
- Use only the manufacturer-approved charger for your scooter, and replace damaged chargers with those from the same manufacturer or reputable sellers to prevent overcharging.
- Put the charger on a non-combustible surface during charging.
- Avoid covering the battery pack and charger during charging to prevent overheating and fire.
- Charge within the specified voltage to prevent overcharging and subsequent ignition.
- Charge the battery in the temperature range of 4°C – 43°C (39°F-110°F) to avoid electrochemical reactions that may lead to fire or explosion.
- Modern batteries have a built-in Battery Management System, unplug the charger once the battery is charged.
- Unplug the charger if you notice a foul smell, smoke, or extreme heat during charging.
- Install a smoke detector or heat alarm in the charging area.
- Allow 5-10 minutes for the battery to cool down after charging before riding.
- Wait for an hour before charging the battery after use to ensure it cools down.
- Refrain from charging the e-scooter while sleeping or when away from home.
- Use un-coiled extension leads for charging.
- Avoid charging or storing the e-scooter near flammable objects or materials such as vinyl, wood, fabric, and paper.
Take a look at my guide on how to charge your electric scooter for all the detailed steps.
Storing your electric scooter

When you are storing your electric scooter you should consider the following tips:
- Avoid storing your e-scooter in excessively cold or hot environments. Store it at around 59°F / 15°C and refrain from leaving it in the kitchen or under direct sunlight for an extended period to prevent thermal runaway.
- Avoid storing or charging your e-scooter in communal areas or emergency exit routes to ensure a safer escape in case of a fire.
- Store your charger and battery in a dry, ventilated, and clean place.
- If your battery is removable, store it in a fireproof bag.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions when storing your e-scooter and Li-ion battery for an extended period without use.
Maintaining your electric scooter
When you are maintaining your electric scooter you should consider the following tips:
- Test and replace the electrical system, including the battery, regularly. Replace accessories with those from the manufacturer or reputable retailers to ensure safety standards.
- Prevent excessive tension and pressure on your electric scooter to avoid damage to components and the battery, reducing the risk of fire.
- If you spot visible leakage or the battery looks worn out, discolored, or bulged, stop using it right away and replace it.
- Never install damaged or dropped batteries in your scooter, as even one worn-out cell can cause a short circuit and a potential fire.
- Don’t keep your scooter battery completely full or empty. It’s recommended you keep it between 20 and 80 percent.
How do you extinguish an electric scooter battery fire?
If you suspect your e-scooter is defective and may ignite, ensure you and others stay away to avoid smoke, toxic fumes, or explosions.
In case of an uncontrollable fire, call emergency services instead of attempting to extinguish it.
For smaller fires, use an ABC fire extinguisher or if unavailable, submerge the battery in water to cut off oxygen supply and reduce temperature.