In this guide, we will look at the differences between lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, and learn why one of them has become pretty much outdated, while the other one has taken over the world of electronics and gadgets.

Lithium-ion batteries outperform lead-acid counterparts in power, reliability, and durability. They offer higher energy density, lower self-discharge, and a compact design. With a longer lifespan, faster charging, and superior environmental friendliness, they stand as a more advanced option.

Lithium-ion vs lead-acid battery
Lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries are the primary battery types used in electric vehicles.
Lithium-ion batteries, recognized as the superior choice for electric vehicles, set the standard for this mode of transportation.
Despite being somewhat pricier, they offer a lightweight design, high energy density, efficiency, and terminal voltage, among other superior properties.
Lead-acid batteries, while more affordable, often lack the advantages associated with modern battery technologies.
Older and perceived as inferior in terms of capacity, efficiency, charge rate, and weight, lead-acid batteries remain a budget-friendly alternative.
Lithium-ion battery: The basics

A lithium-ion battery, with its carbon-based anode, lithium oxide-based cathode, and lithium salt electrolyte, is a popular choice for rechargeable batteries among electric vehicle enthusiasts. Praised for its compact, lightweight design and low self-discharge, lithium-ion batteries have their advantages.
However, there are considerations. Charging a lithium-ion battery at a higher voltage may lead to faster degradation compared to a lead-acid battery. Moreover, these batteries are sensitive to high temperatures, posing a risk of fire and damage if overheated.
While lithium-ion batteries offer enhanced power, they demand additional protection for optimal performance and longevity. If you own an electric scooter, bike, or motorcycle powered by a lithium-ion battery, ensure you maintain safe limits for temperature, voltage, and discharge rates.
How does a lithium-ion battery work?
Lithium-ion batteries works by transporting electrons from one electrode to the other during discharging and charging.
During the discharging process, i.e., when the lithium-ion battery is powering your electric scooter, electrons travel from the negative towards the positive electrode.
During the charging phase, this process is reversed.
Lead-acid battery: The basics
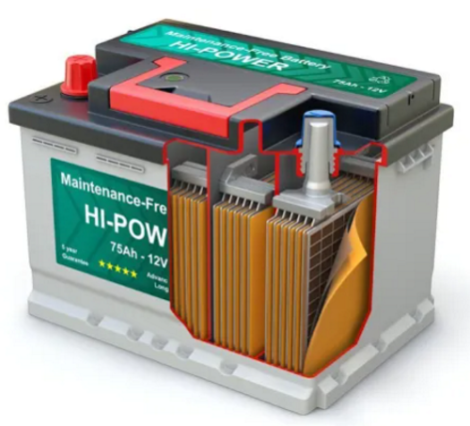

A lead-acid battery, unlike the lithium-ion battery, utilizes lead as a negative electrode, lead oxide as a positive electrode, and sulfuric acid as an electrolyte.
Lead-acid batteries are favored in various transportation devices due to their affordability and high power-to-weight ratio. They are particularly suitable for starter motors in vehicles requiring robust current.
However, compared to lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries are heavier, less efficient, and have lower energy density. They also exhibit longer charging times and a shorter lifespan. These drawbacks explain why many electric vehicle owners opt for lithium-ion batteries.
How does a lead-acid battery work?
The discharging and charging phases of lead-acid batteries involve electrochemical processes similar to those in Li-ion batteries. However, a lead-acid battery operates differently.
Atoms flow from the positive to the negative electrode, while electrons travel from the negative to the positive electrode.
The charging process produces hydrogen and oxygen gases, and the battery voltage reduces between discharging and charging processes.
Lithium-ion vs lead-acid battery differences
| Parameter | Lithium-ion battery | Lead-acid battery |
|---|---|---|
| Energy density | High | Low |
| Capacity | High | Low |
| Efficiency rate | 95% or higher | 80-85% |
| Working temperature | -20 to +60 °C | -10 to +40 °C |
| Depth of discharge | Low | High |
| Size and weight | Compact and lightweight | Bulky and heavy |
| Charge rate | 2-3 hours | 8-9 hours |
| Installation | Easy to install | A bit difficult to install |
| Maintenance | Require less maintenance | Require frequent maintenance |
| Cost | Expensive | Cheap |
| Lifespan | Long | Short |
| Safety and environmental impact | Medium | Medium |
If we take a closer look at the table presented above, we can see that there are several major differences between lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries. These differences include:
Energy density
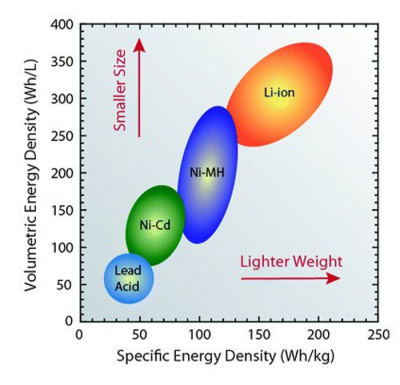
The chart illustrates that lithium-ion batteries have high energy density, a key advantage that renders them indispensable in the realm of modern electric vehicles.
Even the most affordable lithium-ion battery delivers more energy per kilogram than the priciest lead-acid battery, with energy density ranging from 300-500 Wh/kg compared to the lead-acid battery’s 25-35 Wh/kg.
Capacity
In contrast to a lead-acid battery, a lithium-ion battery has greater capacity, enabling it to store more electricity.
Consequently, if you were to travel the same distance on a scooter powered by each of the two batteries, the lead-acid battery would require recharging much sooner than the lithium-ion battery.
Efficiency rate
Once more, a lithium-ion battery exhibits higher energy efficiency compared to an equivalent lead-acid battery. This stems from its capacity to convert energy from electrical to chemical energy during charging and reverse the electrochemical process during discharge.
Using specific figures to illustrate, a lithium-ion battery has 95 percent efficiency. In contrast, the usable energy stored in an equivalent lead-acid battery is rated between 80 and 85 percent.
Depth of discharge
A lithium-ion battery exhibits lower self-discharge than its lead-acid counterpart, meaning the chemical reactions inside it result in less energy loss compared to an equivalent lead-acid battery.
Additionally, lithium-ion batteries maintain low self-discharge both during use and while sitting on the shelf.
This characteristic, along with their ability to hold a charge for an extended period, contributes to the better storage life of lithium-ion batteries.
Size and weight
The preference for lithium-ion batteries among electric vehicle owners is largely due to their compact and lightweight design. In contrast to lead-acid batteries, lithium-ion batteries feature smaller cells composed of the lightweight metal lithium, and their electrolyte is water-free.
Conversely, lead-acid batteries are constructed with the denser material lead, incorporating more cells and a water-based electrolyte.
They necessitate proper ventilation to release gases and prevent overheating in elevated temperatures, contributing to their bulkier and heavier build compared to lithium-ion batteries.
Charge rate

Lithium-ion batteries boast faster charging times compared to lead-acid counterparts.
A single lithium-ion battery pack can be fully charged in 2 to 3 hours, potentially even less with modern quick-charging technology. Additionally, lithium-ion batteries offer the flexibility of partial charging.
In contrast, a lead-acid battery with a similar capacity requires 8 to 9 hours for a full charge. Partial charging is discouraged for lead-acid batteries, as it may lead to sulfating and subsequent damage.
Installation

The compact and lightweight design of lithium-ion batteries makes them easy to install and replace in any electric vehicle. Their sealed cells ensure a leak-proof operation, allowing installation in any position.
In contrast, lead-acid batteries, due to their bulkiness, present challenges in installation. Care must be taken to avoid upside-down installation, which can lead to leakage and venting issues.
Maintenance
Both battery types require maintenance for optimal lifespan, but lithium-ion batteries demand less attention than lead-acid ones.
Lithium-ion batteries incorporate protection circuitry to prevent issues like overcharging, complete discharging, or exposure to high temperatures.
Lead-acid batteries, on the other hand, need periodic de-sulfation of their plates to sustain electrochemical reactions with the electrolyte. Terminal cleaning and regular topping off of the liquid electrolyte with water are also essential.
Furthermore, charging lead-acid batteries necessitates a designated area due to gas emissions during the process. Adequate ventilation systems are required to release the emitted gas safely into the atmosphere.
Cost
A lithium-ion battery is more expensive than an equivalent lead-acid battery. Usually, the extra price is well worth it, however, since the user experience overall is much better with lithium-ion batteries.
Lifespan
Lithium-ion batteries outlast lead-acid counterparts in terms of discharging and charging cycles, nearly doubling their lifespan under equivalent parameters.
A well-maintained lithium-ion battery can endure up to 3000 cycles, while even the top-performing lead-acid batteries typically manage 1200 to 1500 cycles.
Safety and environmental impact
Lithium-ion batteries are safer and more environmentally friendly than lead-acid counterparts. Lead-acid batteries contain corrosive sulfuric acid, risking leakage if overcharged. Their lead electrodes contribute to lead contamination and toxic waste during production, disposal, or recycling.
Overcharging a lead-acid battery may vent oxygen and hydrogen, posing an explosion risk. While fires are possible, their overall fire risk is considered low. Proper precautions can ensure safe and sustainable usage.
In contrast, lithium-ion batteries lack these risks but are sensitive to high temperatures and flammable. Excessive internal heat, exceeding atmospheric dissipation, can lead to thermal runaway and potential explosions.
Pros and cons of lithium-ion batteries
- higher energy density
- greater capacity
- higher efficiency rate
- lower self-discharge
- compact and lightweight design
- faster charge rate
- easier to install
- don’t require frequent maintenance
- longer lifespan
- eco-friendly
- can damage entirely if overcharged or over-discharged
- require internal circuitry system
- expensive
- sensitive to high temperatures
- flammable
Pros and cons of lead-acid batteries
- good efficiency rate
- can produce a sudden surge of electricity
- rugged
- cheap
- low energy density
- bulky and heavy
- take longer to charge
- can’t be partially charged
- harder to maintain
- short lifespan
Are lithium-ion batteries better than lead-acid?
For electric scooters, lithium-ion batteries are typically the best choice due to their high energy density, compact design, lightweight build, substantial capacity, and durability.
Lithium-ion batteries can endure numerous charging cycles without compromising storage capacity or performance. They boast a fast charge rate and can be charged both fully and partially.
On the other hand, lead-acid batteries are prevalent in budget models, larger vehicles, and electric scooters designed for children.