Electric scooter brakes are critical components. They are major safety features of every scooter and that’s why it’s important for us as owners to be familiar with how they work. This guide will go over everything you need to know about them.

How to brake with an electric scooter
Proper scooter braking involves shifting your body weight back, slightly bending your knees, and leaning as if sitting down. You can also pull on the handlebars to brake faster without losing balance.
Use the rear brake first if your scooter has brakes on both wheels and apply both brakes for the shortest stopping distance.
Avoid using the front wheel brake first or exclusively to prevent the scooter from tipping over and causing injury.
If your scooter has a rear fender foot brake in addition to other brakes, use it as an emergency brake, as it’s less convenient for regular use.
Electric scooter brake types

| Brake type | Brake performance | Reliability | Maintenance required | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cable disk | Very good | Very good | Some | Medium |
| Hydraulic | Excellent | Excellent | A lot | High |
| Semi-hydraulic | Very good | Excellent | A lot | Medium-high |
| Drum | Good | Very good | Little | Medium |
| Electronic/regenerative | Average | Very good | Almost none | Low |
| Rear fender foot operated | Poor | Average | Almost none | Low |
Cable disk brakes
Cable disk brakes, or just disk brakes, are the most common type of brakes found in electric scooters today. They provide a good balance of solid braking power, low maintenance, and affordable prices.
How do disk brakes work?

Disk brakes consist of a rotor connected to the wheel and calipers affixed to the rotor’s frame.
These calipers have pistons that engage the brake pads to generate friction against the rotor when you activate the brake lever via cables.
Pressing the lever causes the calipers to push the pistons, which, in turn, engage the pads, bringing your scooter to a stop.
Rotors are made from stainless steel and are very durable, but the pads of the brakes are subject to a lot of friction, which generates a lot of heat, and that wears the pads off.
That’s why they need to be checked frequently and occasionally replaced.
Cable disk brake advantages
Cable disk brakes are versatile and widely known, making them the preferred brake system. Their key advantages include mechanic familiarity, readily available resources for adjustment and repair, and abundant parts.
They also offer strong braking performance and, importantly, allow for easy sensitivity adjustments, providing control over your rides.
Since they are pretty common, disk brakes are often mass-produced, and don’t drive the price of the scooter up too much.
Also, because of their widespread use, they are a tried-and-tested braking system, with proven reliability in all conditions.
Cable disk brake disadvantages
Cable disk brakes are a well-balanced choice for electric scooters with no significant drawbacks. They require maintenance and may need pad replacements, common for high-performance mechanical brakes.
How to adjust my disk brakes?
Cable disk brakes may need to be adjusted as they get older.
If you start hearing some friction or rubbing sounds coming from the wheel, the brake disk may be rubbing against the pads or the wheel, and it may be time to adjust your disk brakes.
Adjusting the brakes will typically involve adjusting the position of the brake pads with an Allen key until they no longer touch the disk.
In most scooters, you will not need to disassemble the brake. See this video for a great walkthrough.
When should I replace my brake pads?
As a rule of thumb, you should measure the thickness of the brake pad with a caliper. The brake pad should be at least 1 mm thick and if it’s smaller than that you should replace it.
Also, consider replacing the pads if they look too old or worn out.
Hydraulic brakes
Electric scooter hydraulic brakes work as a closed vacuum system of hoses, lines, and reservoirs, all filled with special hydraulic oil.
Technically, they also involve a rotor, the same as cable disk brakes do, but they are almost always referred to as just hydraulic brakes.
How do hydraulic brakes work?

When you pull the brake lever, it pushes a piston through the hose.
Since liquids can’t be compressed, the oil forces the calipers to move the pistons, which, in turn, push the brake pads against the wheel’s rotor, creating friction and slowing down the wheel.
Releasing the brake allows the fluid to return to its original position in the closed system, releasing the brake pads.
Hydraulic brakes advantages
Hydraulic brakes have the best stopping power out of all brake types. That makes them the safest brake type for electric scooters.
Also, they are very reliable and rarely suffer malfunctions, which further solidifies them as the safest braking type.
And, like other mechanical disk brakes, they are often simple to adjust and set to the desired sensitivity level you require.
Hydraulic brakes disadvantages
Hydraulic brakes offer superior stopping power but require occasional maintenance (bleeding) due to the hydraulic system.
They are mechanically complex and involve higher production costs, making them common in premium models rather than budget scooters.
Are hydraulic brakes worth it?
The worth of hydraulic brakes, with their superior performance and reliability, depends on personal preference. If safety is a priority, they are a valuable choice.
I find cable disk brakes sufficient for my needs, and while hydraulic brakes offer smoother performance, they’re not a necessity for me when choosing a scooter.
However, for a premium scooter, I’d prefer hydraulic brakes.
Are hydraulic brakes better than cable?
Hydraulic brakes will almost always be better than cable brakes in terms of performance, reliability, durability, and safety. The only possible exception here is comparing the best-quality cable brakes with the lowest-quality hydraulic brakes.
Are hydraulic brakes easy to maintain?
Out of all the brake types, hydraulic brakes are the most difficult to maintain.
Still, the process can be relatively straightforward if you have the right tools and a little bit of know-how.
Here is a video of RoadRunner Scooter explaining how to easily adjust hydraulic brakes.
Semi-hydraulic brakes

Semi-hydraulic brakes combine features of both cable and hydraulic brakes, using a closed system with hoses, reservoirs, and pistons, with a cable between the lever and caliper.
They offer a good balance of stopping power and lower maintenance.
Drum brakes
Drum brakes are made out of a drum and a backplate assembly, attached to the wheel of the scooter. The drum is usually made from cast iron, which is very durable and conducts heat well.
This is one of the rarest brake types in electric scooters.
How do drum brakes work?

The drum rotates with the wheel, while the stationary backplate houses various components.
Brake shoes, like brake pads, have friction-inducing material, known as brake lining, covering their outer surfaces.
A cylinder with pistons, driven by hydraulic pressure during braking, pushes the brake shoes against the drum, creating friction to slow down the movement.
Releasing the brake triggers retaining springs to return the system to its original position.
Drum brakes advantages
One of the major advantages of drum brakes is that they require very little maintenance.
Also, the internals of the brake are protected by the drum, so they are isolated from water, dirt, and the elements, which can significantly prolong their lifespan.
Drum brakes disadvantages
Drum brakes are not as strong as disk or hydraulic brakes, and that’s the primary reason why they’re rarely found in scooters today.
Also, they are somewhat heavier and bulkier than other brake types, and add a lot of volume to the wheel, and a bit more weight to the scooter in general.
What is the difference between drum brakes and disc brakes?
Disk brakes outperform drum brakes with shorter braking distances, more adjustments, and easier repairs. Drum brakes require less maintenance and are often more reliable.
Electronic brakes
Most budget scooters today will come with electronic brakes.
How do electronic brakes in electric scooters work?
Electronic brakes function by cutting power to the motor, causing quick loss of momentum and generating friction to halt wheel movement.
They are active on the motorized wheel, and in dual-drive scooters, on both wheels. In some models, you can disable or adjust the strength of the electronic brake system if it’s not the primary brake.
Regenerative braking (energy recovery)
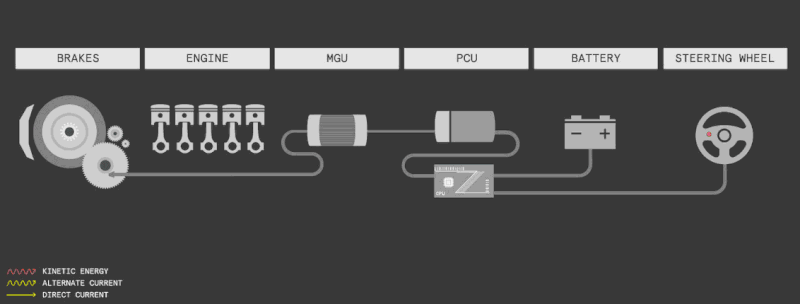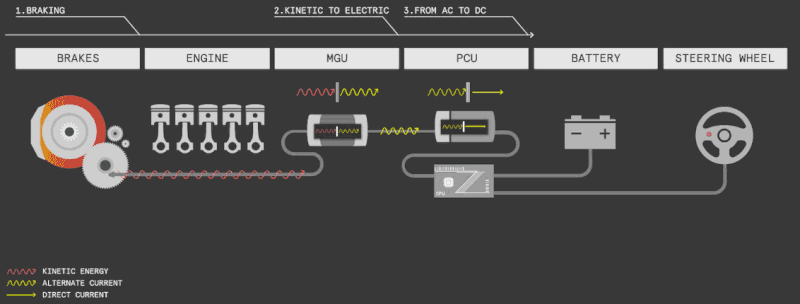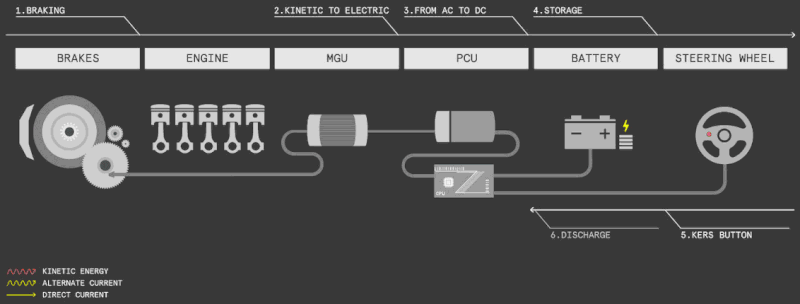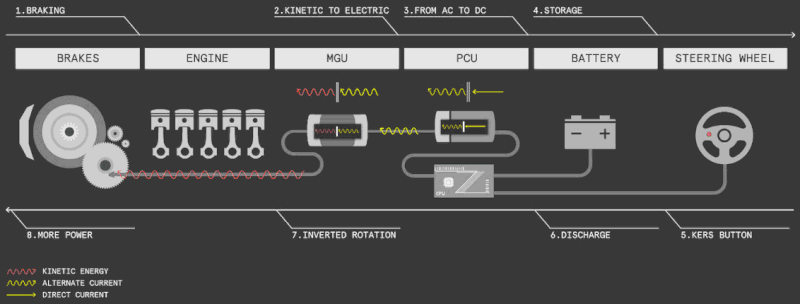
The majority of scooters with electronic brakes also come with the regenerative braking feature, also known as the energy recovery feature, or KERS (kinetic energy recovery system).
Regenerative braking converts the scooter’s kinetic energy into electricity to recharge the battery, effectively capturing energy from the moving wheel.
It’s like a free lunch, utilizing existing momentum to generate additional power.
Regenerative braking typically recovers a small amount of battery energy, with estimates suggesting an extension of 5-10% in the best cases.
In many scooters, you can adjust the energy recovery level or turn it off in the settings to suit your preferences.
Here is a video of Eloi explaining how regenerative braking works.
Electronic brakes advantages
Electronic brakes are low-maintenance, typically requiring no user intervention. If an issue arises, which is rare and often related to the motor rather than the brakes, seeking expert assistance is advisable.
Also, since electronic brakes usually just come with the motor instead of being considered a separate feature, they don’t really drive the price up that much.
Finally, electronic brakes usually come with an energy recovery feature, which is always nice to have.
Electronic brakes disadvantages
Electronic brakes are not very strong and don’t really provide a good braking distance. They are often meant to be a support braking system and are not a replacement for good cable or hydraulic brakes.
Rear fender foot brakes
Several electric scooter models today come with the foot-operated brake. This type of brake is usually found in budget scooters.
How do rear fender foot brakes work?

Rear fender foot brakes work on the simplest principle out of all the scooter brake types.
By simply pressing the rear mudguard with one of your feet, you create friction between the mudguard and the rear wheel, which slows down and stops the scooter.
Foot brakes advantages
The only real advantage of rear foot brakes is their simplicity, which will result in them barely requiring any maintenance at all.
Foot brakes disadvantages
Rear fender foot brakes are simple but offer limited stopping power.
They are primarily meant for emergency use when primary brakes fail. Using them can be challenging as it requires balancing while pressing backward with one foot.
Also, because their underlying mechanism is quite crude, they are prone to defects, mostly the fender breaking off, or sometimes getting stuck.
In some scooters, a rear fender foot brake can be beneficial, but top-quality scooters usually rely on stronger braking systems, and many riders don’t prefer this brake type.
Anti-locking braking system (ABS)
The anti-lock braking system (ABS) is an add-on feature in some brake systems that prevents wheel lock and skidding during braking, maintaining steering control.
It’s an automated system that monitors individual wheel speeds and adjusts brake pad pressure to prevent loss of steering control or wheel lock.
ABS is commonly used in vehicles, including scooters. It’s a valuable safety feature that can prevent accidents. Many scooters with electronic brakes include ABS, and you can often adjust or deactivate it based on your preference.
The details of how exactly ABS works are a bit more complex, and outside the scope of this article. In case you want to understand the concept of ABS and how it works in more depth, check out this video.
Front brakes, rear brakes, and brake redundancy
Electric scooters typically have either rear brakes or both front and rear brakes. Using just front brakes at high speeds is unsafe, as it increases the risk of tipping over and injury.
Scooters with multiple brake systems offer “brake redundancy” for added safety.
Brake malfunctions can occur, so having multiple brake systems is a valuable safety feature. More diverse brakes enhance safety further.
Between the two wheels and the several different brake types, there are many possible brake system configurations. Some of the most popular brake configurations are:
- just a rear disk brake
- rear disk brake and an electronic brake in the wheel where the motor is
- rear and front disk brakes
- rear and front disk brakes, and a rear fender foot brake
- just an electronic brake in the wheel where the motor is
- semi-hydraulic brakes on both wheels
- fully hydraulic brakes on both wheels
Are front brakes more effective than rear brakes?
Front brakes offer greater stopping power as the forward shift in the center of gravity naturally applies more force and pressure to the front wheel during braking.
Using the front brakes maximizes this advantage, increasing friction and reducing stopping distance.
Which brakes wear out first?
The brakes used more will wear out sooner.
Generally, rear brakes see more use, requiring more frequent replacement. If both brakes are used equally, the front brakes wear out first due to increased pressure and friction.
Brake controls
Besides the front vs rear brake, there’s another dimension related to the brake systems in electric scooters, and that’s the control used for engaging the brakes. There are three main methods of activating a brake:
- lever
- regular button
- thumb button
Levers commonly activate brakes, such as disks, drums, or hydraulic brakes.
Buttons, like thumb buttons, are typically for electronic brakes, and a single button may engage multiple braking systems simultaneously.
Electric scooter brake upgrade
Upgrading your electric scooter’s brakes requires basic DIY skills, patience, and the right tools.
The most common upgrade is from standard mechanical cable disk brakes to hydraulic brakes.
Ensure compatibility with your scooter before attempting the upgrade, as most models lack manufacturer-specific brake upgrades, and hydraulic brakes can be expensive.
For beginners, it’s often better to consider purchasing a scooter with hydraulic brakes. If you proceed with the upgrade, follow the experiences of others who have done it before.
Generally, it involves removing the old brake system and installing the new one, though complications may arise. If the new brakes fit your scooter, it’s a matter of patience.
The following video does a great job of walking you through the process of installing hydraulic brakes on a Xiaomi M365 step by step.
How to check scooter brakes?
Regularly check your brakes and compare their performance to the initial baseline.
For a basic check, start with a slow ride to test the brakes and then gradually increase your speed.
For advanced diagnostics, measure the braking distance from full speed when you first get the scooter, before any adjustments or heavy use.
This establishes your baseline performance.
When conducting a detailed check, measure the braking distance again. If the two distances differ significantly, consider brake replacement.
Best electric scooter brake manufacturers
Many budget electric scooters typically have basic brakes, featuring generic mechanical disk cable brakes and electronic brakes.
These disk brakes, even from popular brands like Xiaomi and Ninebot, are solid but not from specialized brake manufacturers.
Electronic brakes are often integrated with the motor and don’t function as a separate braking system.
Higher-end scooters use hydraulic brakes from reputable brake specialists, which can include bicycle brake manufacturers. These brakes leverage similar principles and mechanisms, ensuring top-quality performance on electric scooters.
The best manufacturers of high-quality brakes for electric e-scooter brakes are Buckloss, Zoom, and Nutt.
Brake defects are not a very common type of electric scooter defect. They account for just 0.4% of all serious defect types reported in the first year of the scooter’s usage.
In scooters with one brake, it’s usually on the rear wheel, and the brake lever or button can be on either handlebar. If the scooter has two brakes, the front brake lever or button is typically on the left handlebar, unless it’s designed for left-handed use, in which case the front brake may be on the right handlebar.
In scooters with brakes on both wheels, the rear brake lever is usually on the right handlebar. If the scooter has only one brake (usually the rear), the brake lever or button is typically on the left handlebar.
In general, expect that you may need to change your brakes every 400 mi / 650 km on average.